Loyalty programs are one of the best ways to build your brand community—the ultimate retention tool for businesses in any industry. In the past, we’ve compiled lists of amazing loyalty program examples in several different industries but we thought it was time to create a larger collection of the absolute best ecommerce loyalty and rewards programs around in every industry.
The following list was put together to inspire you when putting together your own loyalty program and brand community, no matter what you sell or what stage you’re at.
Table of Contents
- Arts & Crafts industry
- Beauty & Cosmetics industry
- Clothing & Fashion industry
- Electronics industry
- Food & Drink industry
- Health & Supplements industry
- Home & Garden industry
- Furniture industry
- Jewelry & Accessories industry
- Pet Supplies industry
- Sports & Recreation industry
- Toys & Games industry
Best loyalty programs in the Arts & Crafts industry
Wallack Art Supplies’ Orange Circle Rewards

Program highlight: meaningful, value-added rewards
Making your rewards program a natural extension of your brand is a must, and Wallack’s Art Supplies does that perfectly through its Orange Circle Rewards loyalty program. From a branded explainer page, clever VIP tier names, and on-theme language such as “Rewards Designed For You”, customers know the loyalty program is closely aligned with the brand values. Wallack’s takes it a step further with meaningful value-added rewards for its best customers, such as presales to demos and classes, free access to certain demos, and VIP shopping events.
Diamond Art Club’s Diamond Insider Rewards
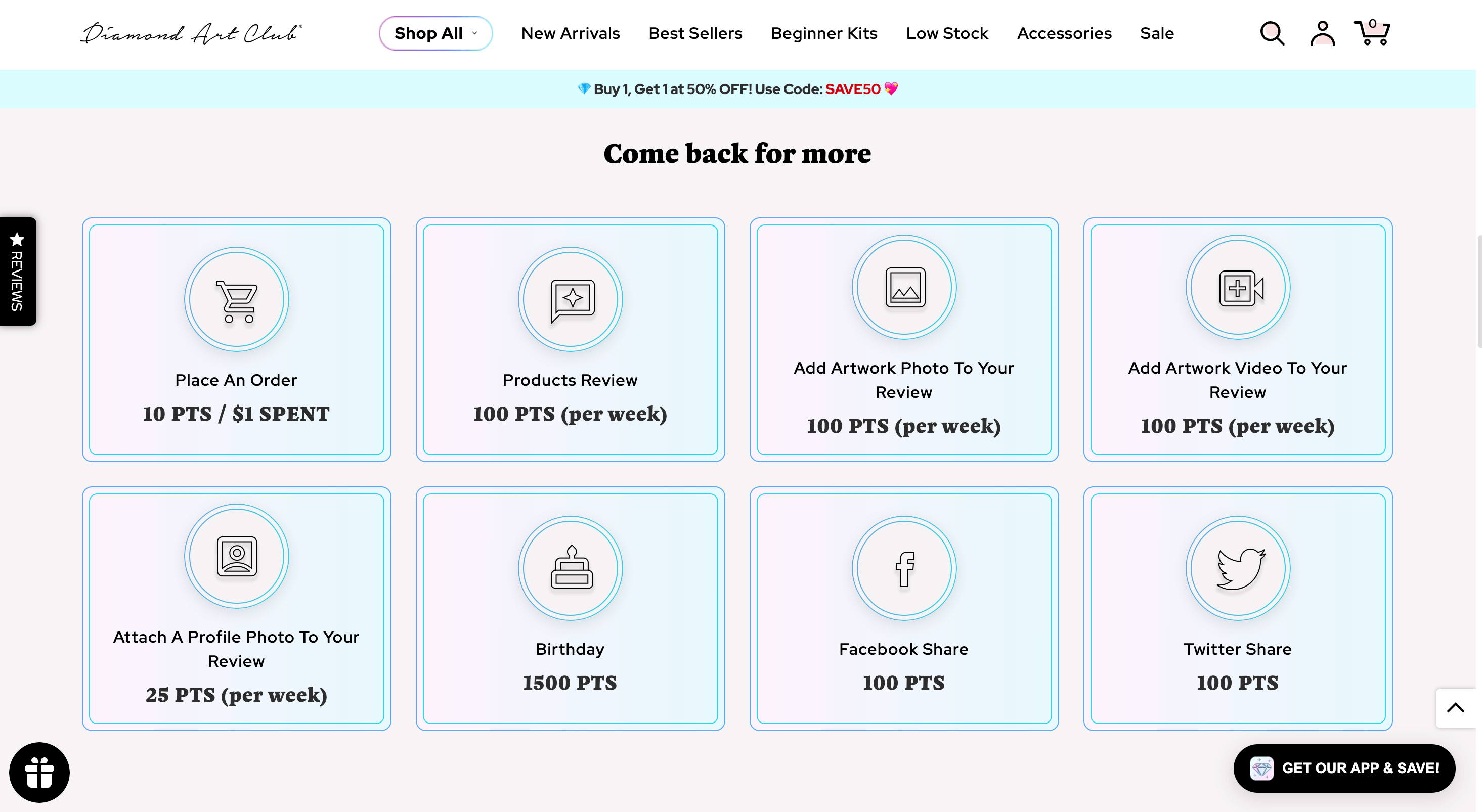
Program highlight: incentivized user-generated content
In an industry as visual as the arts and crafts industry, social proof is an invaluable asset. Diamond Art Club incentivizes this type of user-generated content in its loyalty program by offering reward points for product reviews with additional points available for photo and video reviews. Customers not only get to show off their artwork to a like-minded community and inspire others—they get rewarded for doing so!
Best loyalty programs in the Beauty & Cosmetics industry
Blume’s Blumetopia

Program highlight: branded immersive explainer page
Skincare and personal care brand Blume takes the cake for one of the best rewards program explainer pages we’ve seen. When customers visit this page, they’re taken on a virtual journey to Blumetopia through visual and audio effects, as well as inviting, playful language. Through its tiered VIP program, Blume also offers community-driven experimental rewards like access to the brand’s close friends’ Instagram story and a private Facebook group.
Sephora's Beauty Insider
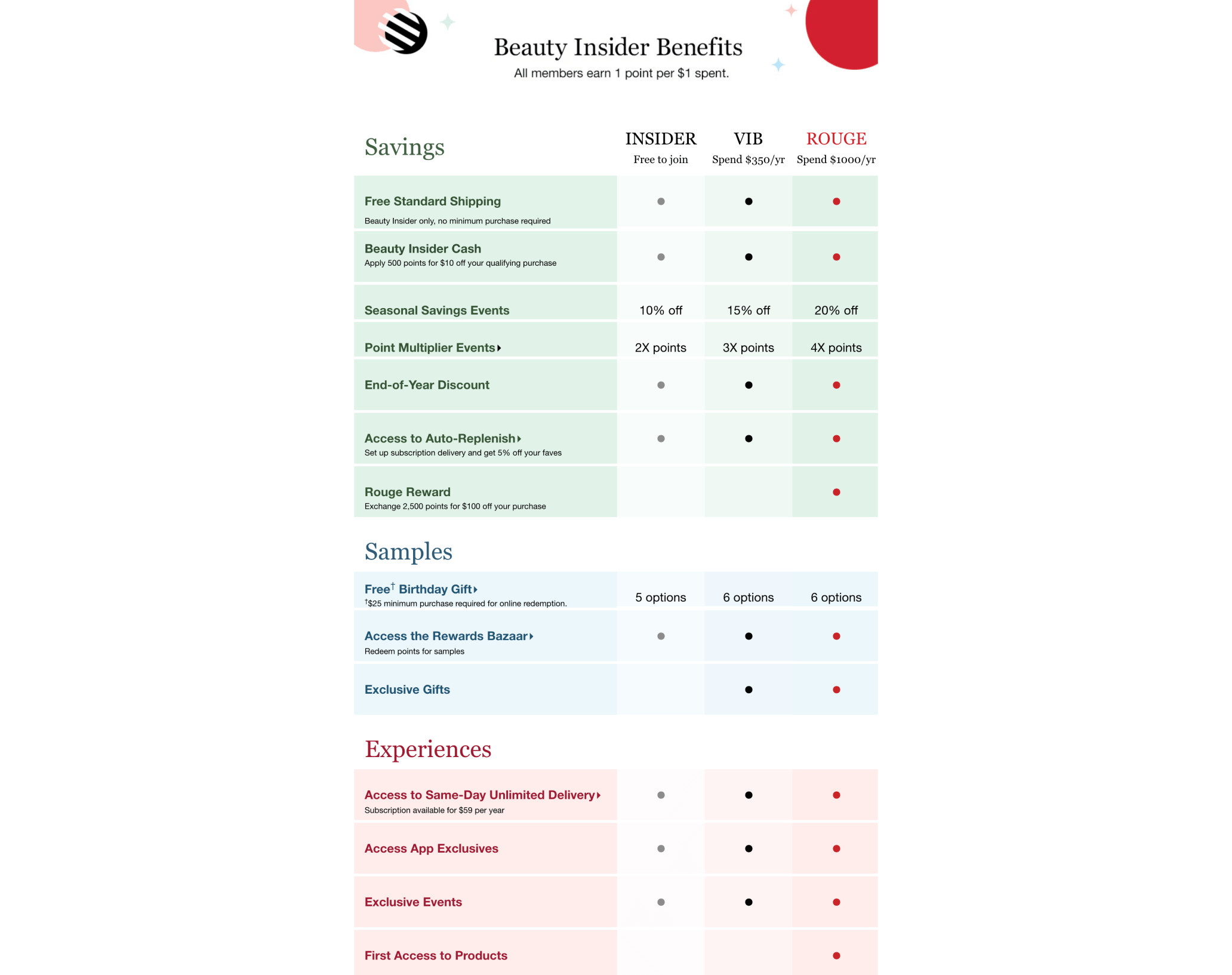
Program highlight: reward exclusivity
Sephora’s Beauty Insider is undoubtedly one of the best ecommerce customer loyalty programs out there. Most of the community’s success stems from their VIP tiers’ high level of exclusivity and a variety of status-based rewards. VIB Rouge members are treated to rewards that play on their status in the program, including invites to parties and community events. Community members can unlock access to VIB Rouge (the highest tier in their program) and its incredible benefits after spending $1,000 in one calendar year, showing their status as fully dedicated members of the Beauty Insider community.

Best loyalty programs in the Clothing & Fashion industry
Nordstrom's Nordy Club
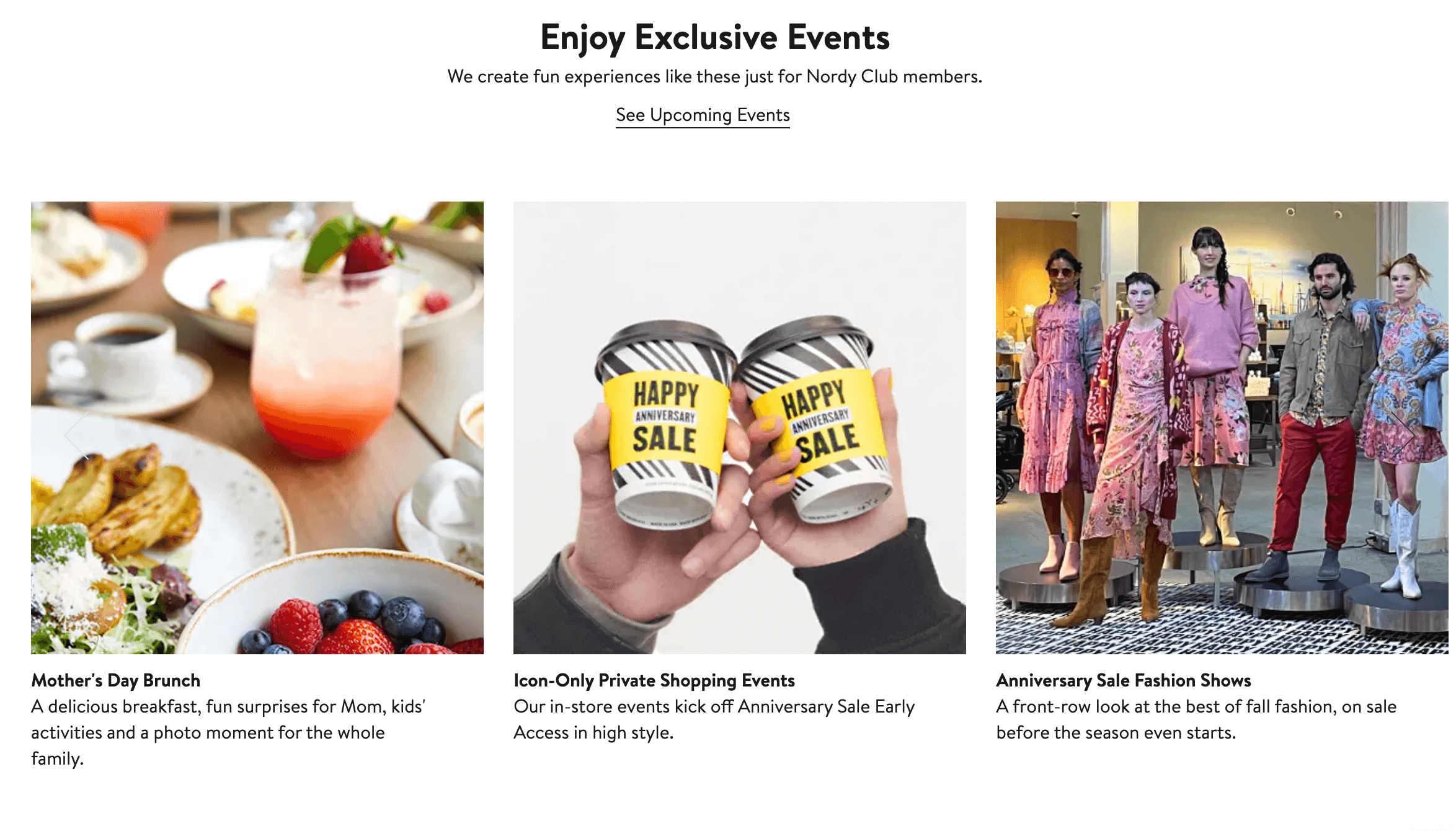
Program highlight: luxurious experiential rewards
While Nordstrom’s Nordy Club offers a ton of features that make the loyalty program great, there is one that stands out—its comprehensive portfolio of luxurious experiential rewards. With 3 VIP tiers, Nordstrom rewards its top tier VIP members with unique experiences like in-home stylists, various double points days, and invites to events IRL like its annual Mother’s Day brunch or seats at fashion shows. This example of aspirational marketing at work is great because it plays upon their community member’s desire to be part of an exclusive club.
Esther & Co’s Royal Rewards
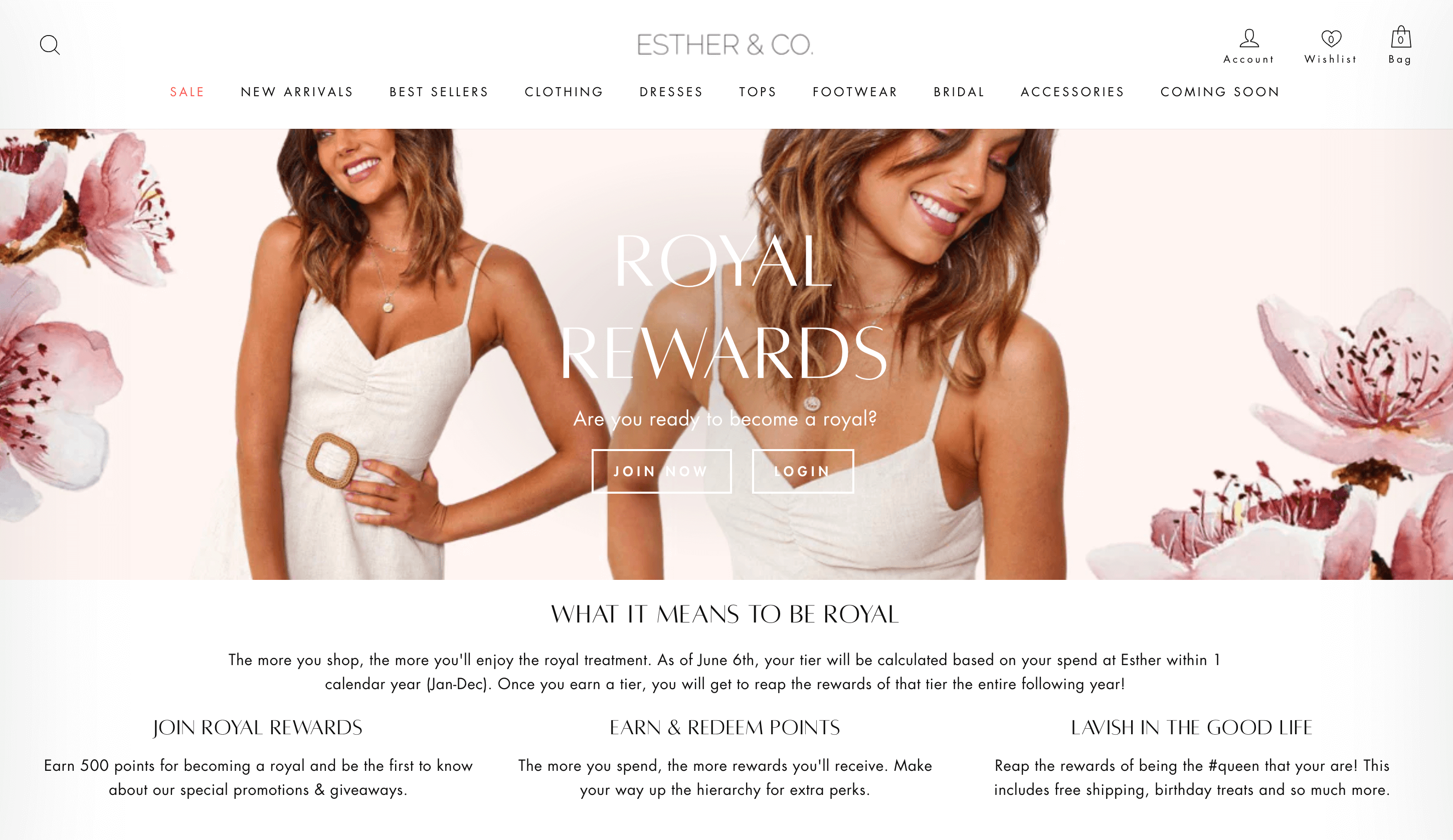
Program highlight: supercharged point earning from sharing
Esther & Co. has built one of the most rewarding brand communities around with their Royal Rewards program. They’ve created standard VIP tiers that provide more points per dollar spent as you move through the ranks, but the most valuable part of their program comes from how they’ve made it so rewarding for members to help build the community. With a $10 reward per successful referral and 50 points per social share, it’s easy to see how they’ve built such a strong brand community.

Best loyalty programs in the Electronics industry
Casely’s VIP Rewards Program
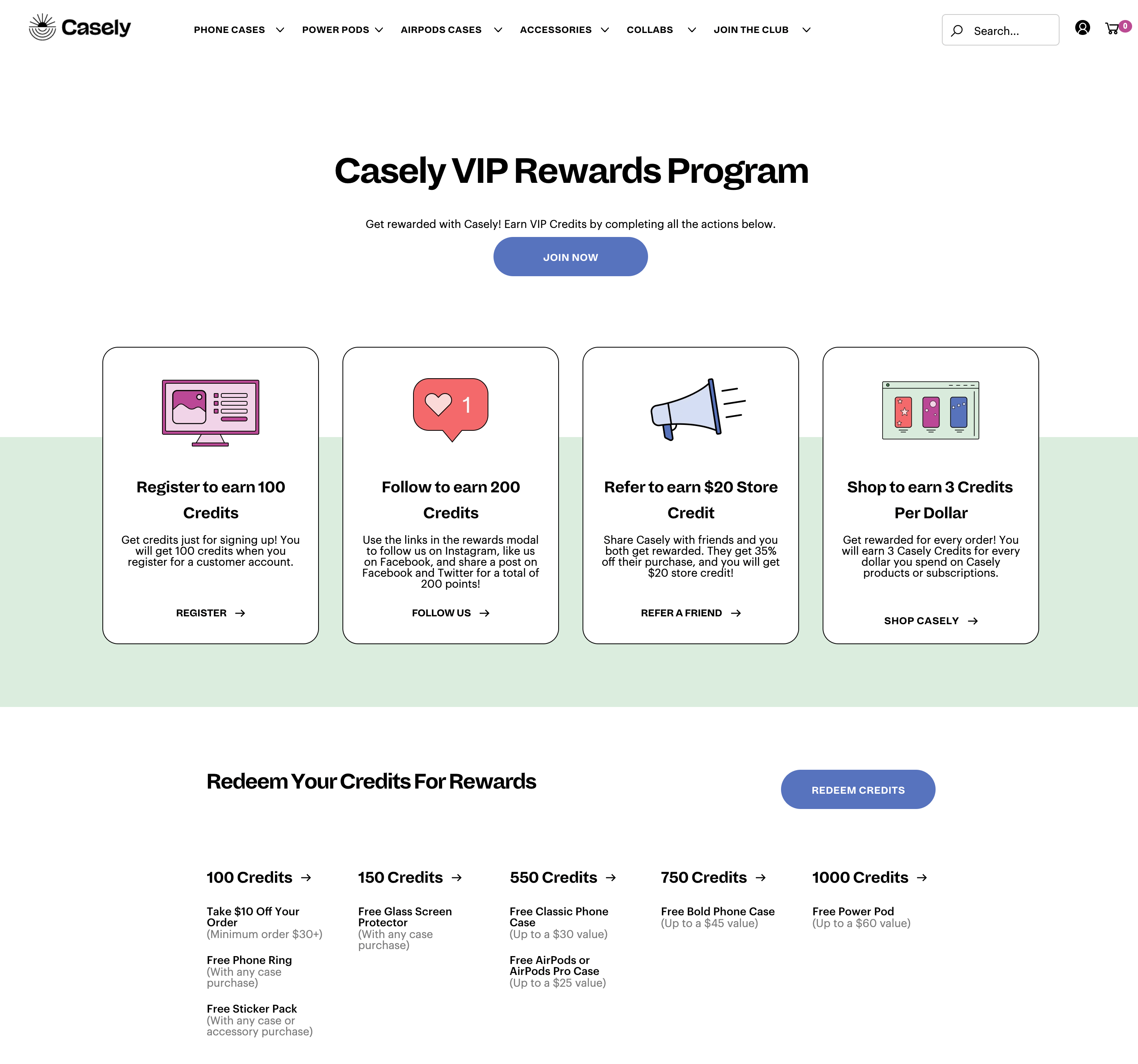
Program highlight: rewards catalog
Phone case and accessory brand, Casely, has done a great job at making its rewards program exciting to generate repeat purchases in a low purchase frequency industry (how often do you buy a new phone case, after all?). Community members can earn points for completing a variety of different actions, including signing up in the first place, completing a purchase, or following on social media. The best part, however, is the rewards catalog, which lets community members spend points on merchandise as opposed to simply getting a traditional discount. Offering these “points products” is a great way to create a loyalty program that feels exclusive and gets community members invested in the brand, so they keep coming back for more.
Nintendo’s My Nintendo Rewards
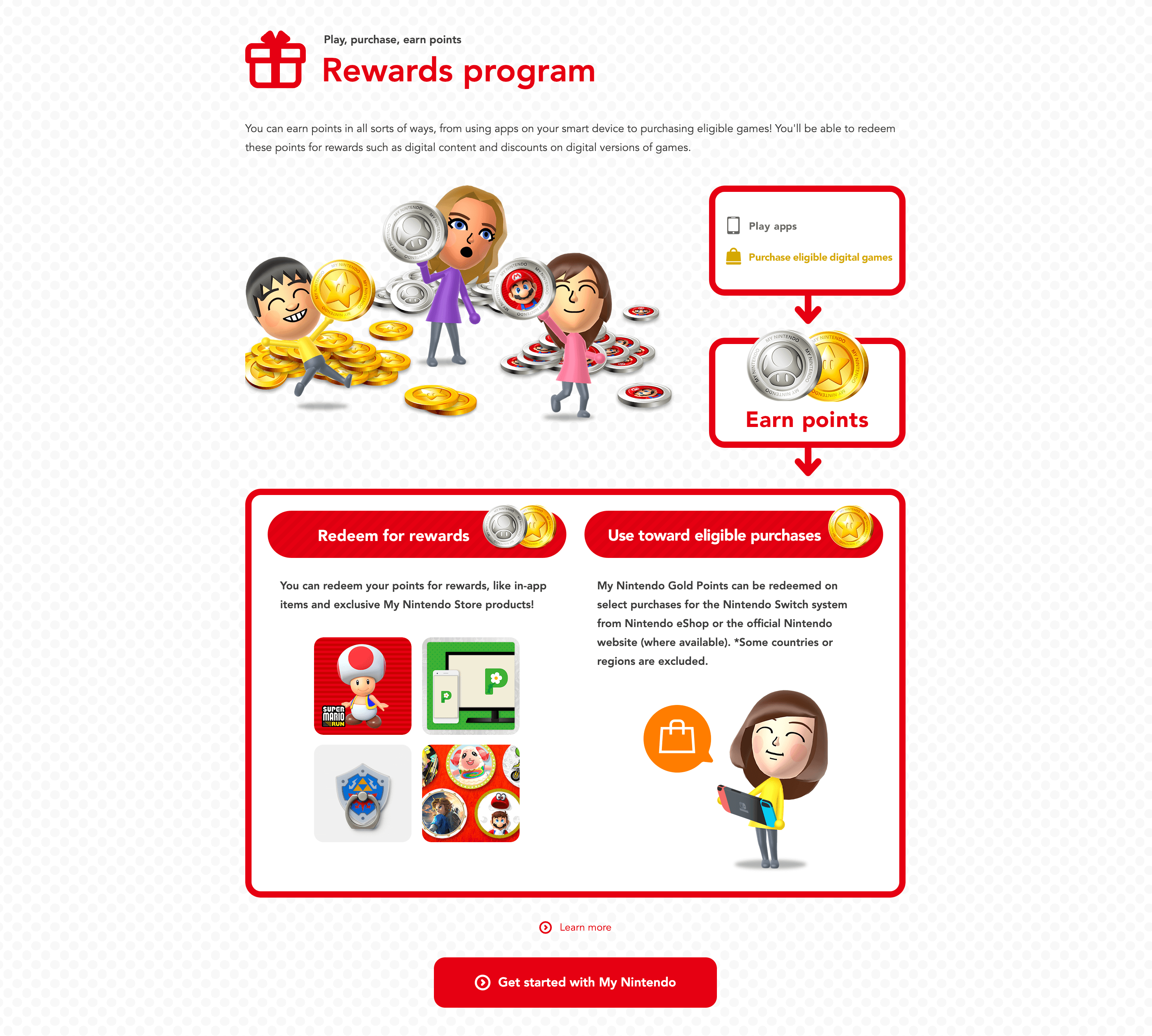
Program highlight: gamification at every stage
As the creator of some of the most iconic video games of all time like Mario Kart, Zelda, Minecraft, and more, Nintendo has turned its customer loyalty program into an exciting game of its own. The My Nintendo Rewards program gives customers a variety of ways to earn digital Gold or Platinum point tokens just like they can in virtual games. By playing Nintendo apps or purchasing eligible digital games, My Nintendo members can cash their coins in for in-app items, tangible exclusive My Nintendo store products, or even eligible games through the various e-stores. From the points currency to program branding, Nintendo’s loyalty program feels just like another one of its famous games.
Best loyalty programs in the Food & Drink industry
Starbucks Rewards
Program highlight: mobile app
No list of the best ecommerce customer loyalty programs would be complete without Starbucks’ Rewards Program. The community they’ve created around the Starbucks brand experience is incredible and rewarding, offering members free in-store refills, free foods and drinks, and the ability to order ahead through the mobile app. Through the same app, customers track their progress towards reward levels, view weekly bonus star challenges, and even earn bonus stars for linking an eligible payment method. With the ability to access the entire program at your fingertips, Starbucks Rewards has created an excellent customer loyalty experience.
EATABLE Popcorn’s Pop Perks
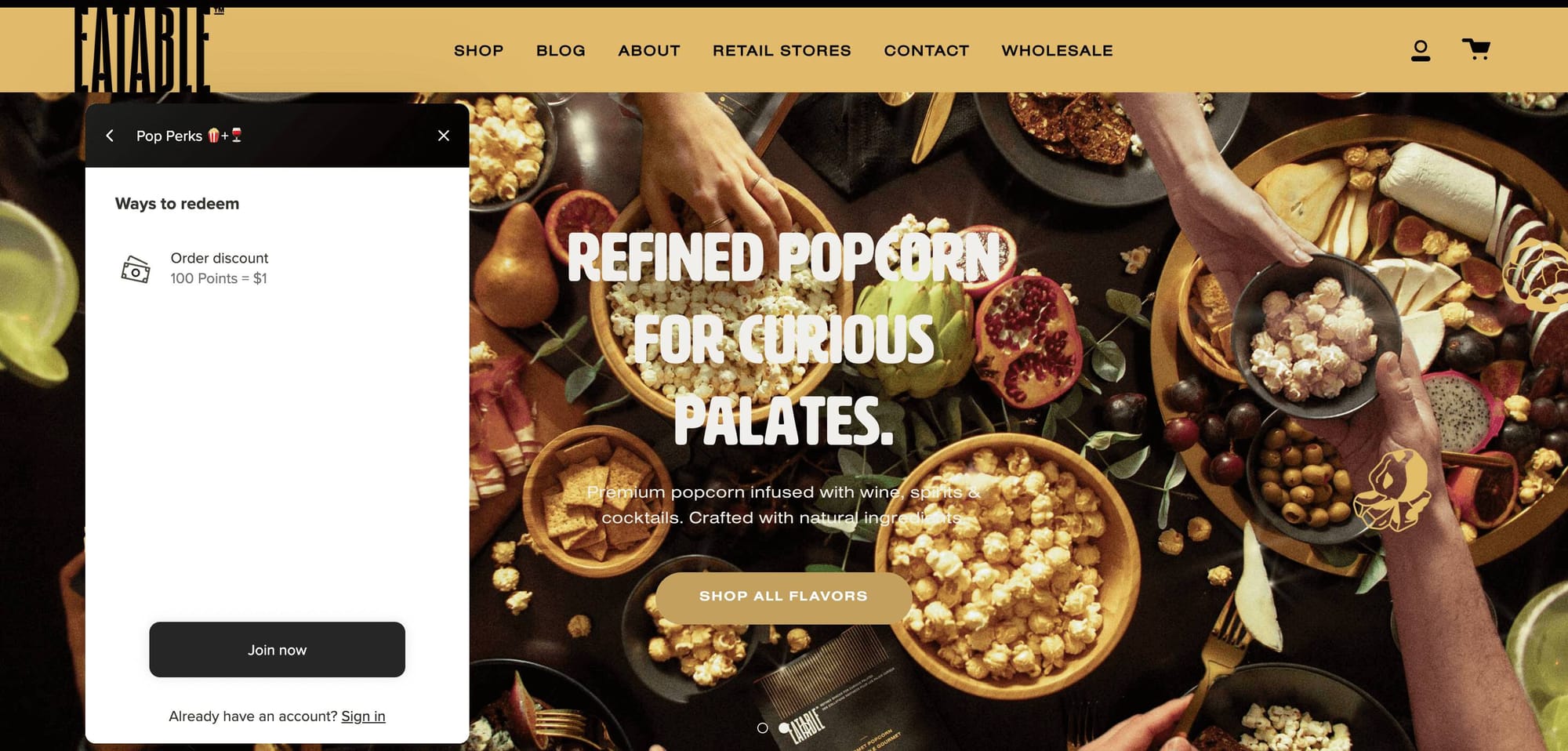
Program highlight: flexible redemption values.
The food and beverage industry is the perfect candidate for a points program. With high purchase frequency and the potential for strong brand loyalty, gourmet snack brand EATABLE Popcorn leveraged the power of points. Co-founder Charlene shares, “Since our inception, we’ve been able to increase our customer repeat purchase rate significantly—over 10% lift.” One way EATABLE keeps customers coming back is by offering a flexible rewards redemption configuration where 100 points = $1 off. With a relatively low-priced product, this gives customers the flexibility to save a few bucks each time they shop or bank up their points for a huge popcorn haul!

Best loyalty programs in the Health & Supplements industry
Jimmy Joy Rewards
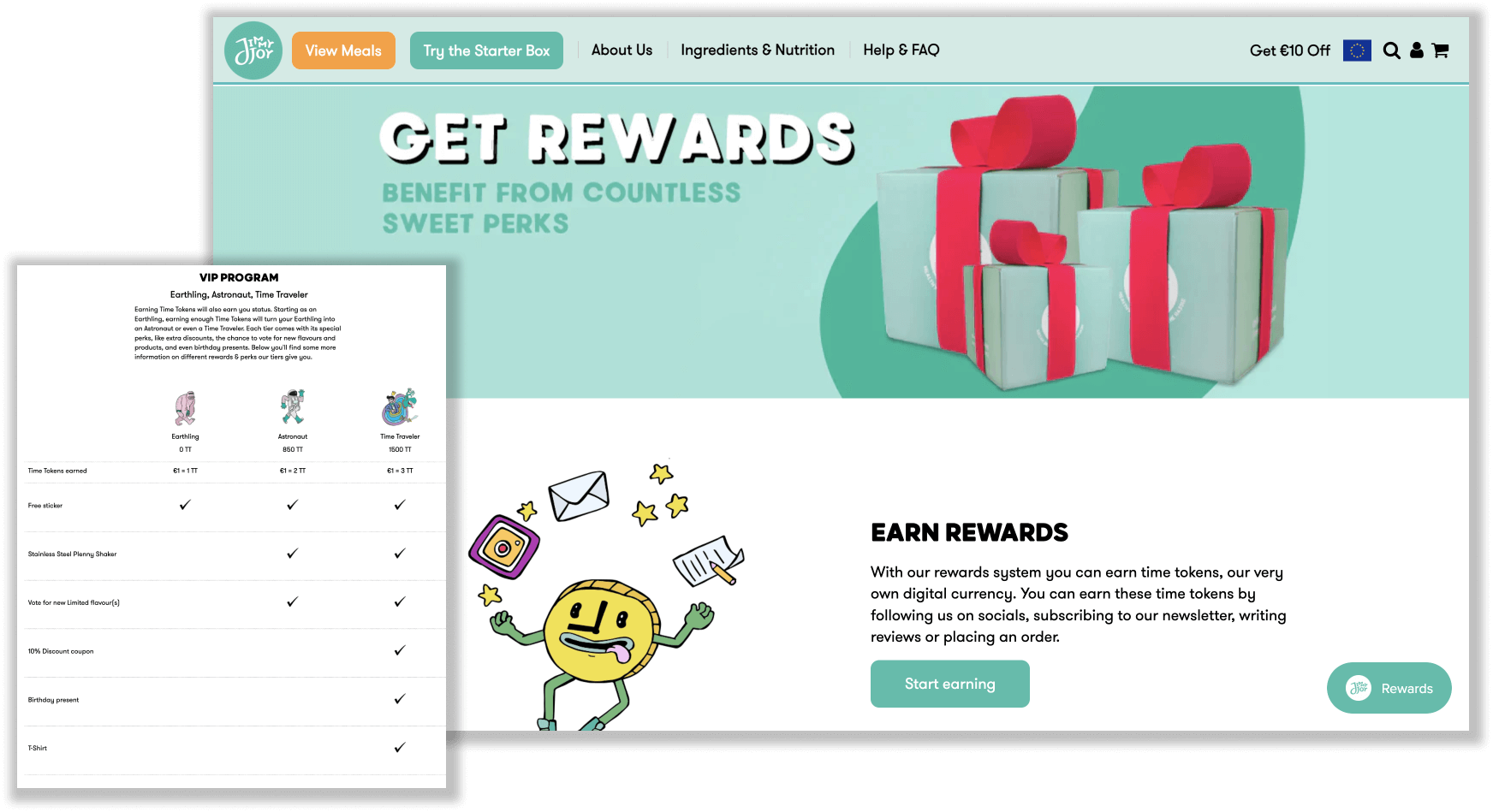
Program highlight: memorable, branded VIP tiers
If your entire brand is centered around evoking upbeat, positive, happy emotions, your customer loyalty program should be no different. One brand that understands this more than anyone is health and supplement brand, Jimmy Joy. With the word “joy” literally in the name, Jimmy Joy Rewards keeps the good vibes going through bright colors, branded icons, playful language, and funny VIP tiers customers can strive for. From Earthling to Time Traveler, customers can work their way up to a higher status with more exclusive perks.
Lumity’s LumityCollective Rewards
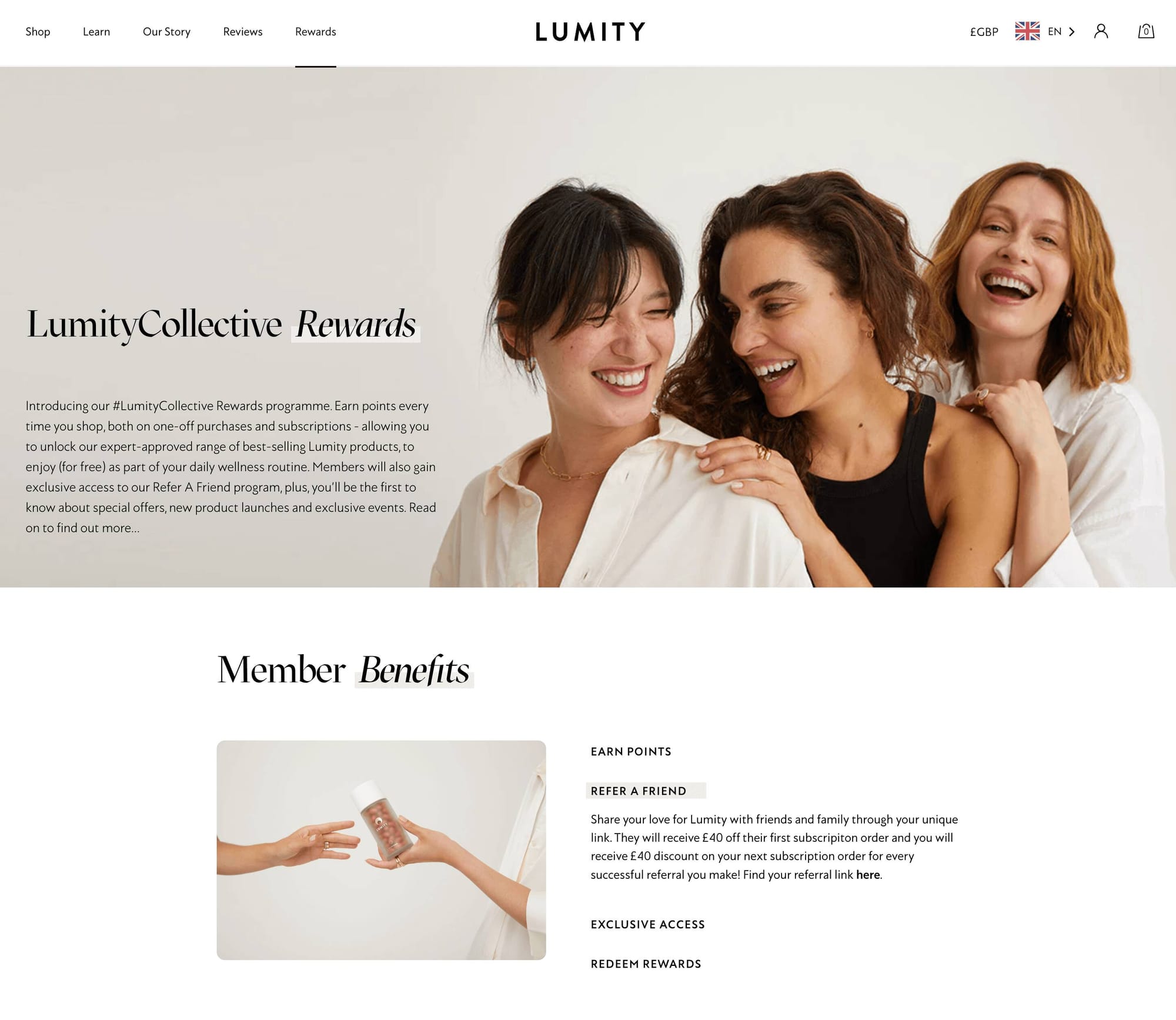
Program highlight: generous referral rewards
When it comes to your health and well-being, you’re going to do your research before trying any old product. This is why the power of a referral from someone you know and trust is so valuable in the health and supplement industry. U.K.-based supplement brand, Lumity, takes advantage of this with a generous referral program, part of its LumityCollective Rewards. Both parties involved in a successful referral receive a £40 reward—making product trial less risky for newcomers and giving existing customers a nice discount on a product they already love!

Best loyalty programs in the Home & Garden industry
Indigo's Plum Rewards
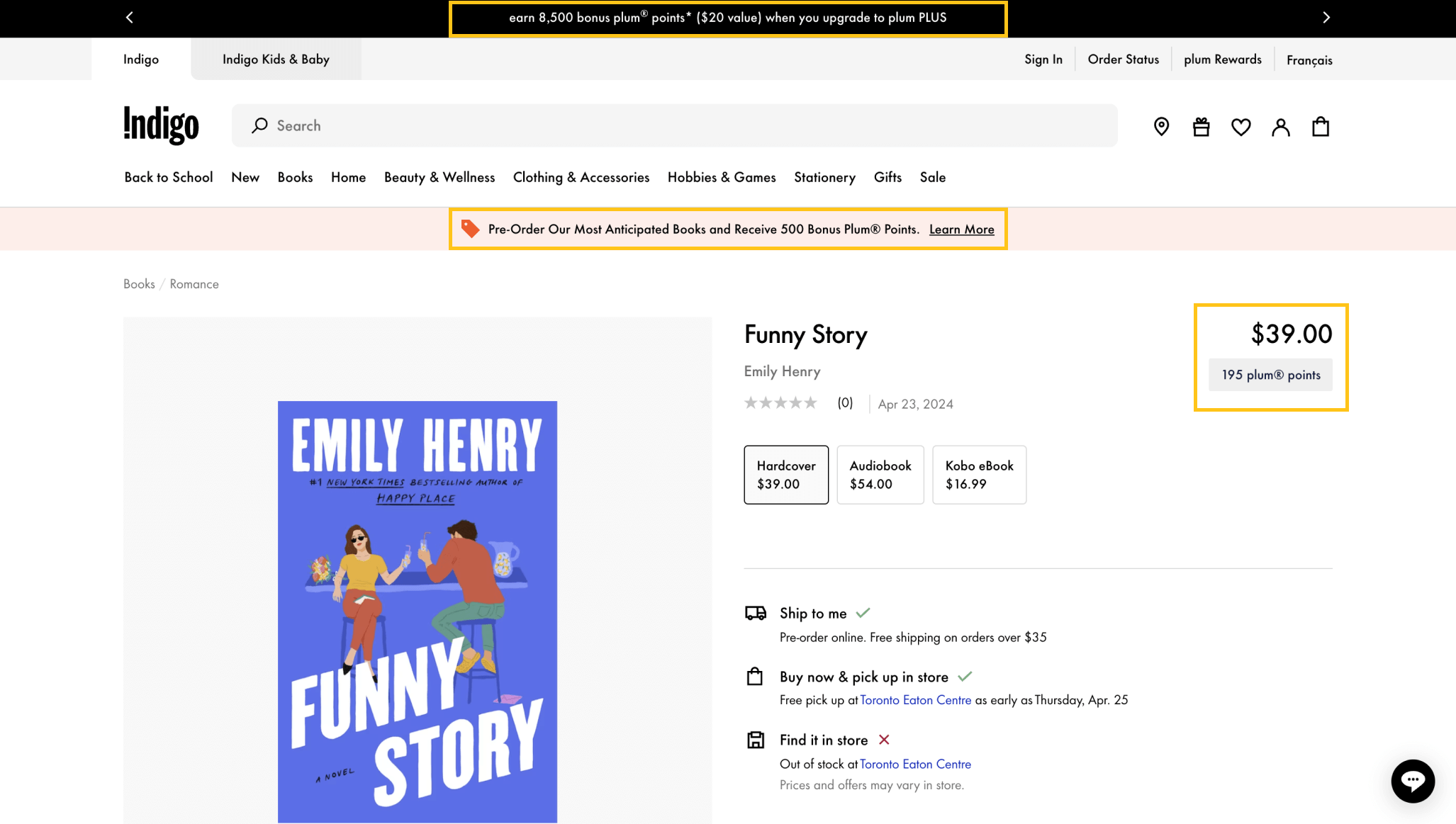
Program highlight: points earning integrated into the entire website
Indigo’s Plum Rewards helped the brand build an online community by offering additional points for community members to make purchases online and in-store. The best thing is that customers can see how many points they will earn with every purchase they make on their website, as well as any bonus points up for grabs. Indigo also holds regular online-only point multiplier events, further motivating customers to spend money on their website (where their margins are higher) rather than in-store.
Sage x Clare’s Whole Lotta Lovers Loyalty Club
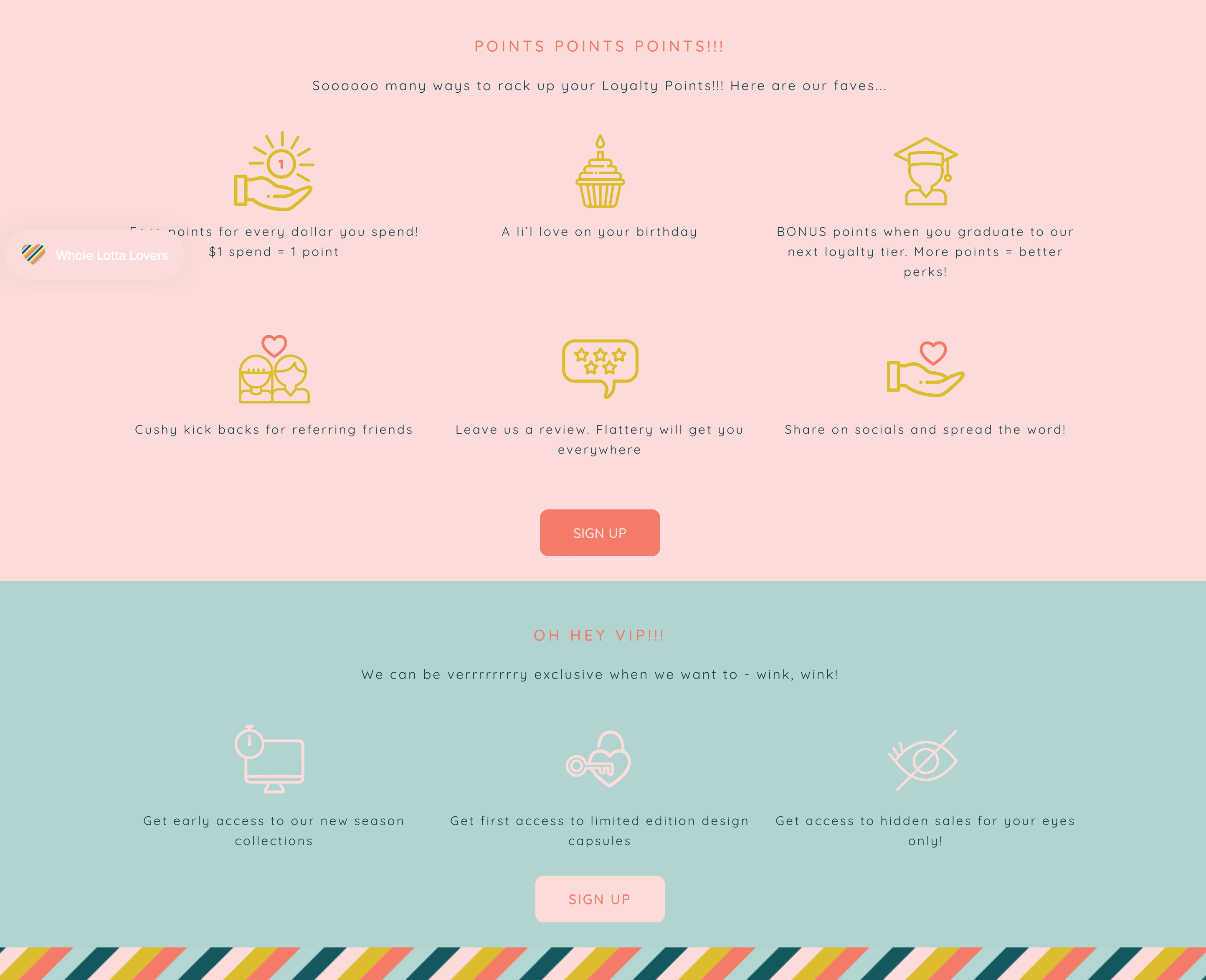
Program highlight: inviting and playful language on the explainer page
Just as you wouldn’t let your product range go out of style, you shouldn’t let your loyalty program communications get out-of-date either. Sage x Clare is a homeware store with an eclectic collection of boho, handmade artisanal products. With bright, colorful, unique designs, it lives and breathes its brand slogan, “With a Whole Lotta Love.” Its appropriately named customer loyalty program carries this ethos by using playful friendly language on every aspect of its explainer page. From its CTA of “ rewarding rrreallly good taste with super special perks”, to cute points earning explanations like “a li’l love on your birthday” and “leave us a review.” Flattery will get you everywhere,” Sage x Clare delivers the information clearly and memorably.
Best loyalty programs in the Furniture industry
IKEA Family
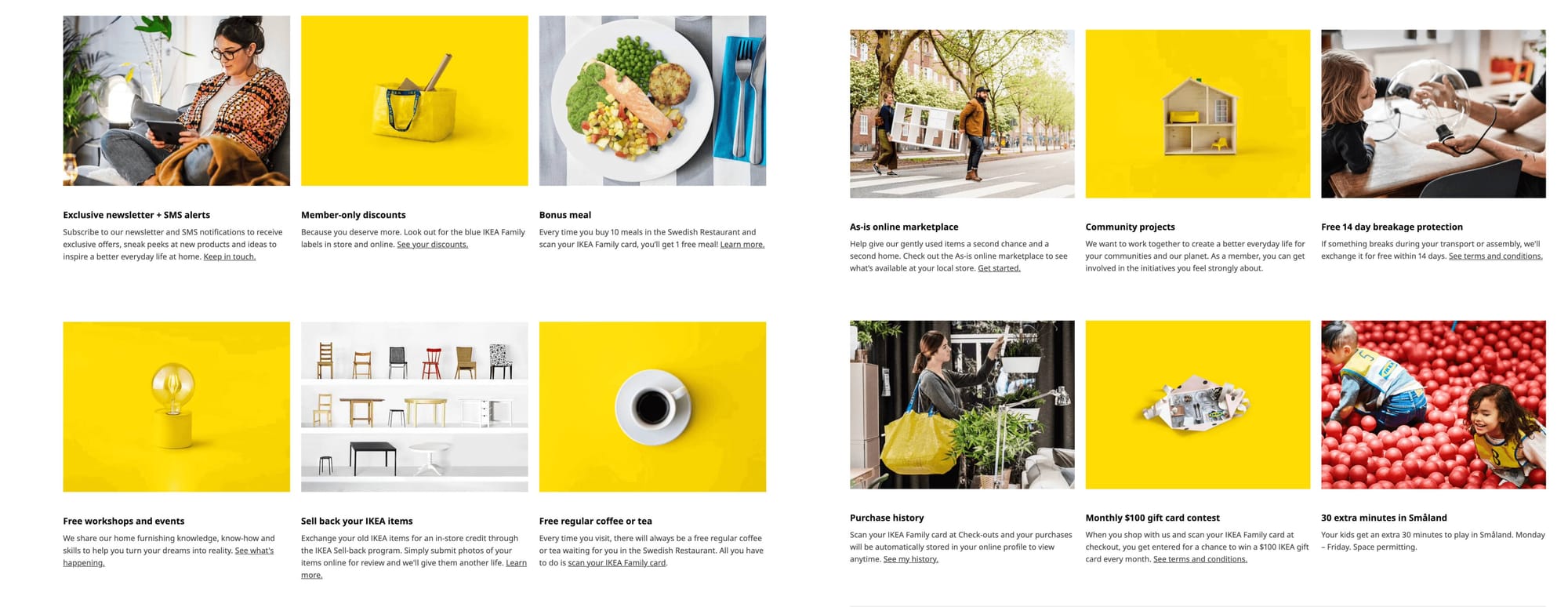
Program highlight: customer-oriented program benefits
Legendary Swedish furniture store IKEA is loved by millions around the globe for a variety of reasons from its affordable simple, good-quality designs to its customer loyalty program, IKEA Family. IKEA is loved by a wide demographic of customers from college students to first-time parents because the products are simple enough to appeal to tastes and styles. IKEA recognizes this through the benefits offered to its IKEA Family members. From extra time in the playground for parents shopping with kids, to access to its as-is online marketplace for eco-friendly or price-conscious consumers, there is a benefit that speaks to everyone.
Debongout’s Loyalty Program
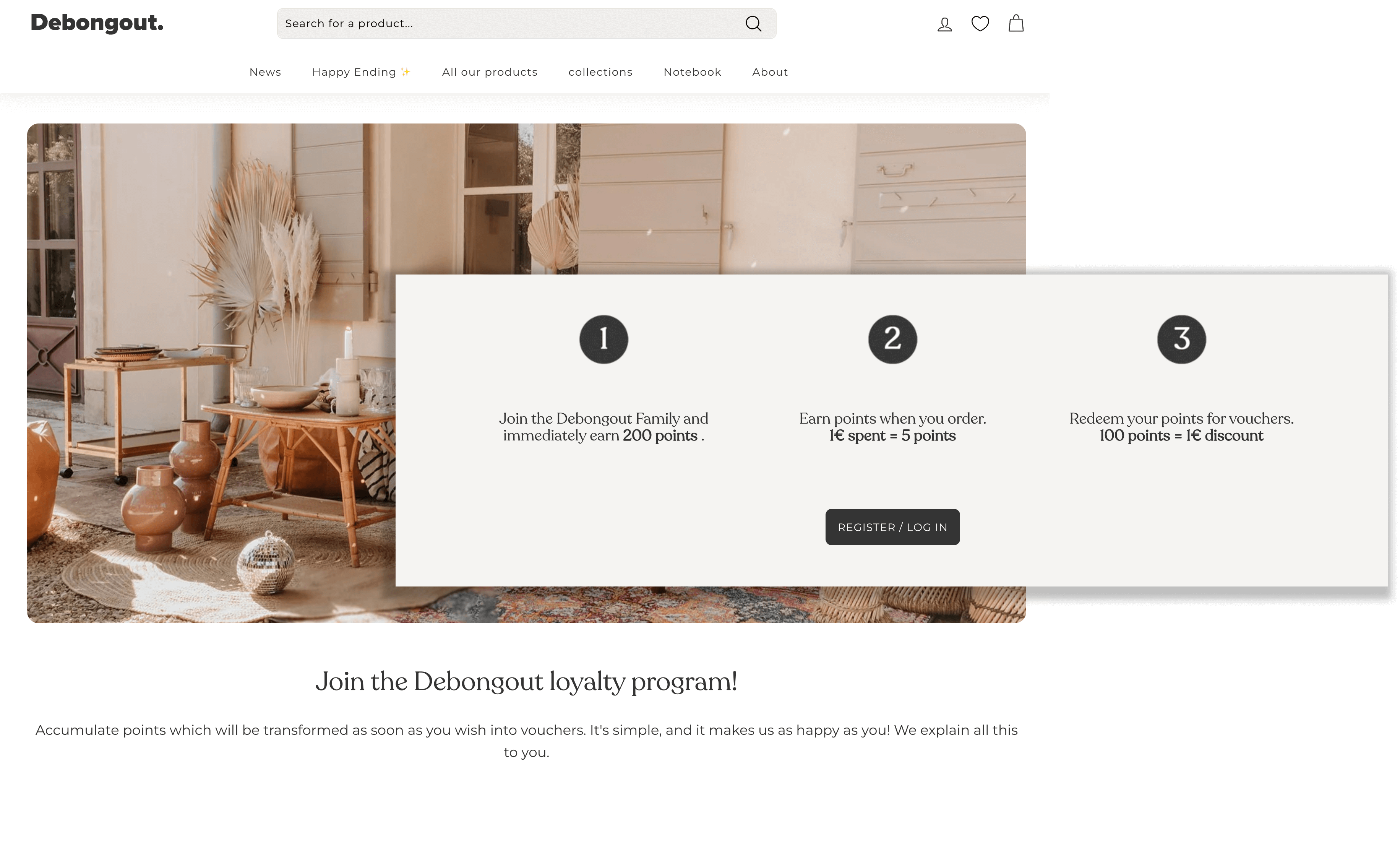
Program highlight: healthy points ROI for customers
Furniture is an industry with a famously low purchase frequency—but that doesn’t mean you can’t create a great customer loyalty program. The key here is proper rewards program configuration, and French vintage furniture store Debongout has cracked the code. Through its points program, customers can earn 5 points for every euro spent and redeem 100 points for 1 euro off their next purchase. Applying a little loyalty program math, that is a 5% ROI for every euro spent with the brand, well within Smile’s recommended range of 3%-10%! This will be enough to keep customers thinking of Debongout’s for its next big furniture purchase while protecting the brand’s margins.
Best loyalty programs in the Jewelry and Accessories industry
Swarovski Club
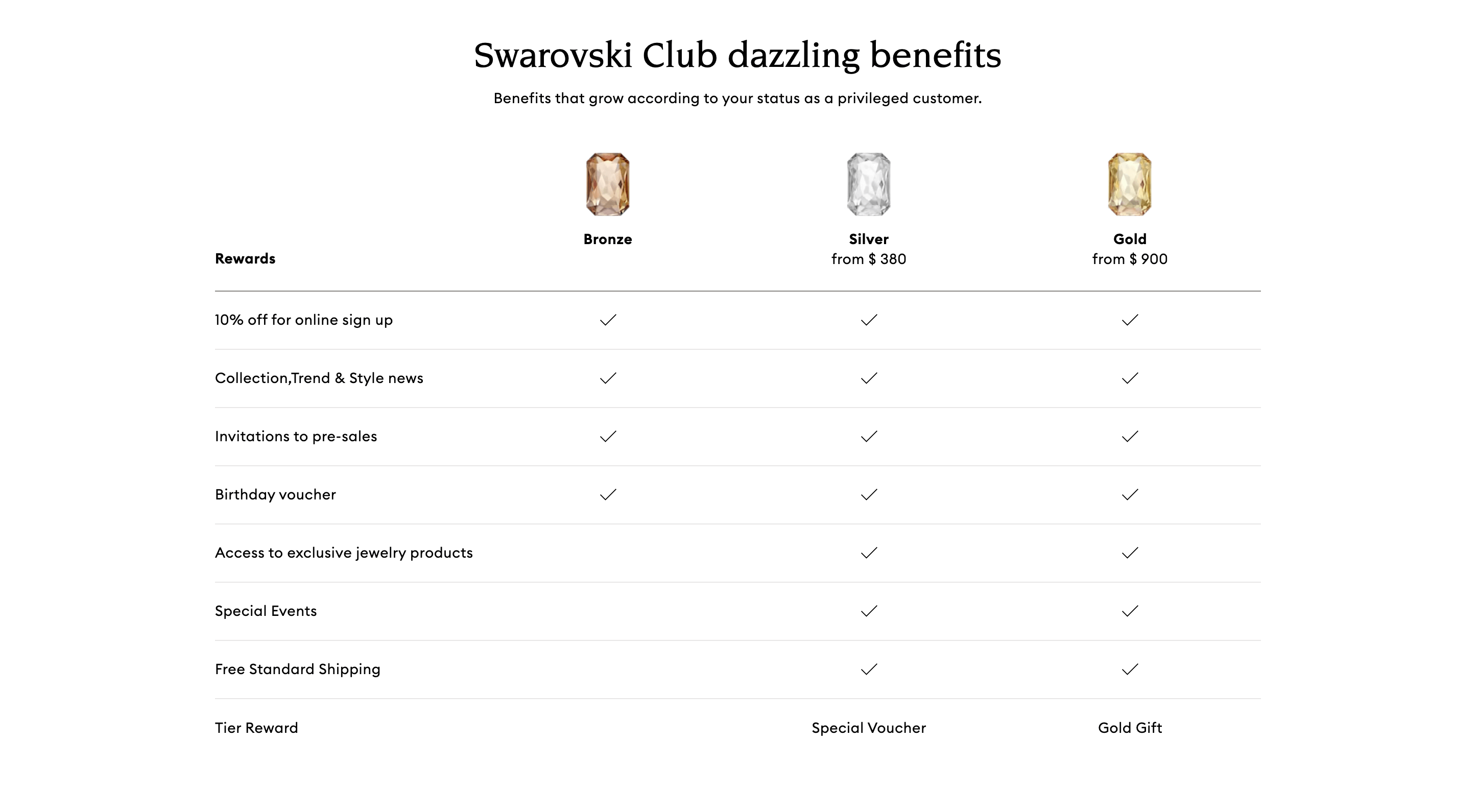
Program highlight: status-based VIP tiers
In an industry as luxurious as jewelry and with a brand as elite as Swarovski, status is everything. This is why a tiered VIP program is the perfect addition to its Swarovski Club customer loyalty program. Customers can work their way up from the bronze tier, through silver, all the way to gold based on their annual spend. Not only does unlock more prestigious benefits, but the perceived status is a reward in itself for Swarovski’s most privileged customers!
Wanderlust + Co Rewards

Program highlight: rewards for reviews and social sharing
The jewelry industry is visual by nature and customers want to see the products before they buy them—not just on models but on real people as well. This is why rewarding customers for social sharing and leaving reviews is a great loyalty program tool. Wanderlust + Co. does an excellent job at this by offering 30 points for each social share and 10 points per review. This is an easy way for customers to earn points to use towards rewards while providing valuable social proof future customers will rely on.
Best loyalty programs in the Pet Supplies industry
Wüfers’ Cookie Coin Rewards
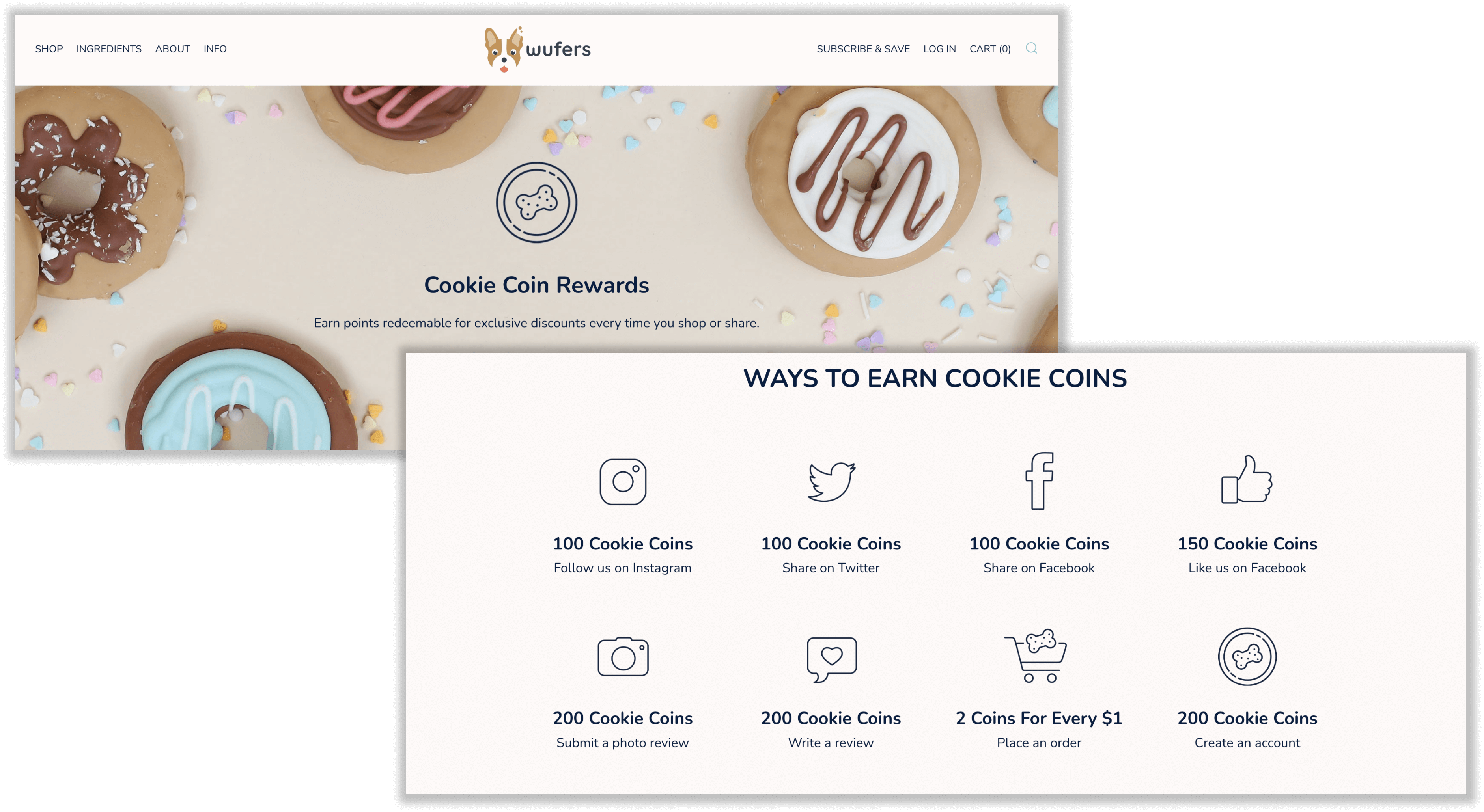
Program highlight: Integrated referral and points programs
Anybody who has a furry friend knows how much pet owners care about their pets. They won’t just buy any old product for them until they know it’s good quality. The pet parent community is an extremely vocal one, so why not use this to your advantage as an ecommerce business? Dog cookie brand, Wüfers does exactly this through its Cookie Coin Rewards program. It combines its points program with a referral program to simultaneously acquire and retain customers for a low cost. Existing customers earn 1000 cookie coins ($10 value) for each new customer they successfully refer (who will get $10 off their first purchase themselves). By giving existing customers points instead of a discount, you give them the option to save their points for an even bigger discount!
Woof & Wonder’s Wonderfam Rewards

Program highlight: omnichannel loyalty program marketing
Ecommerce loyalty programs are a great customer retention tool, but only when implemented effectively. They are not magic tools and need proper marketing and promotion just like any other marketing campaign. Dog accessory brand Woof & Wonder understands this and promotes its Wonderfam Rewards extremely effectively by using channels that align with their customers’ behaviors. With nearly 20K followers on Instagram, Woof & Wonder uses stories to explain how to earn and redeem wonder coins. The results? A happy brand community and successful loyalty program. Founder Lena shares with us, “Customer satisfaction is our top priority, and showing them that we care about their joyful experience has been possible with this program. A happy customer will spread the news to their friends and family!”
Best loyalty programs in the Sports & Recreation industry
Spikeball’s SpikePoints Loyalty Program
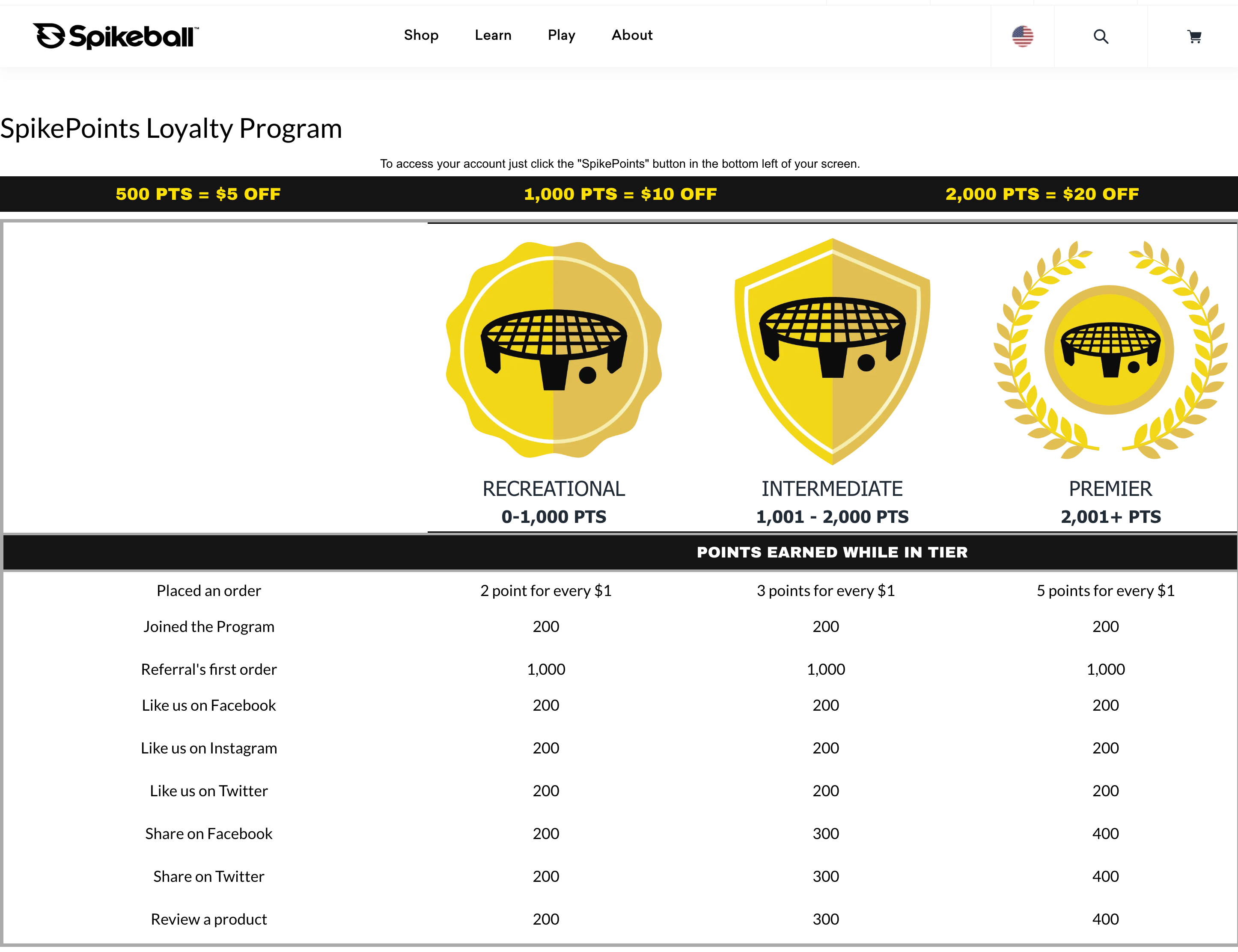
Program highlight: reviews increase in value with VIP tiers
For over a century, humans have played the same classic sports—baseball, basketball, soccer, football, and the list goes on. But every once in a while, a new game is invented that disrupts the game (literally). So how did a brand like Spikeball get thousands of customers to veer away from the classics? Through the power of user-generated content and its customer loyalty program, SpikePoints was a great tool to do so. As customers progress through the 3 VIP tiers, not only do they earn more points per dollar spent, but they also earn more points per review left. New customers are going to trust experienced customers more than newbies so this is the perfect mechanism to solicit those valuable reviews to build credibility!
KYDRA Rewards
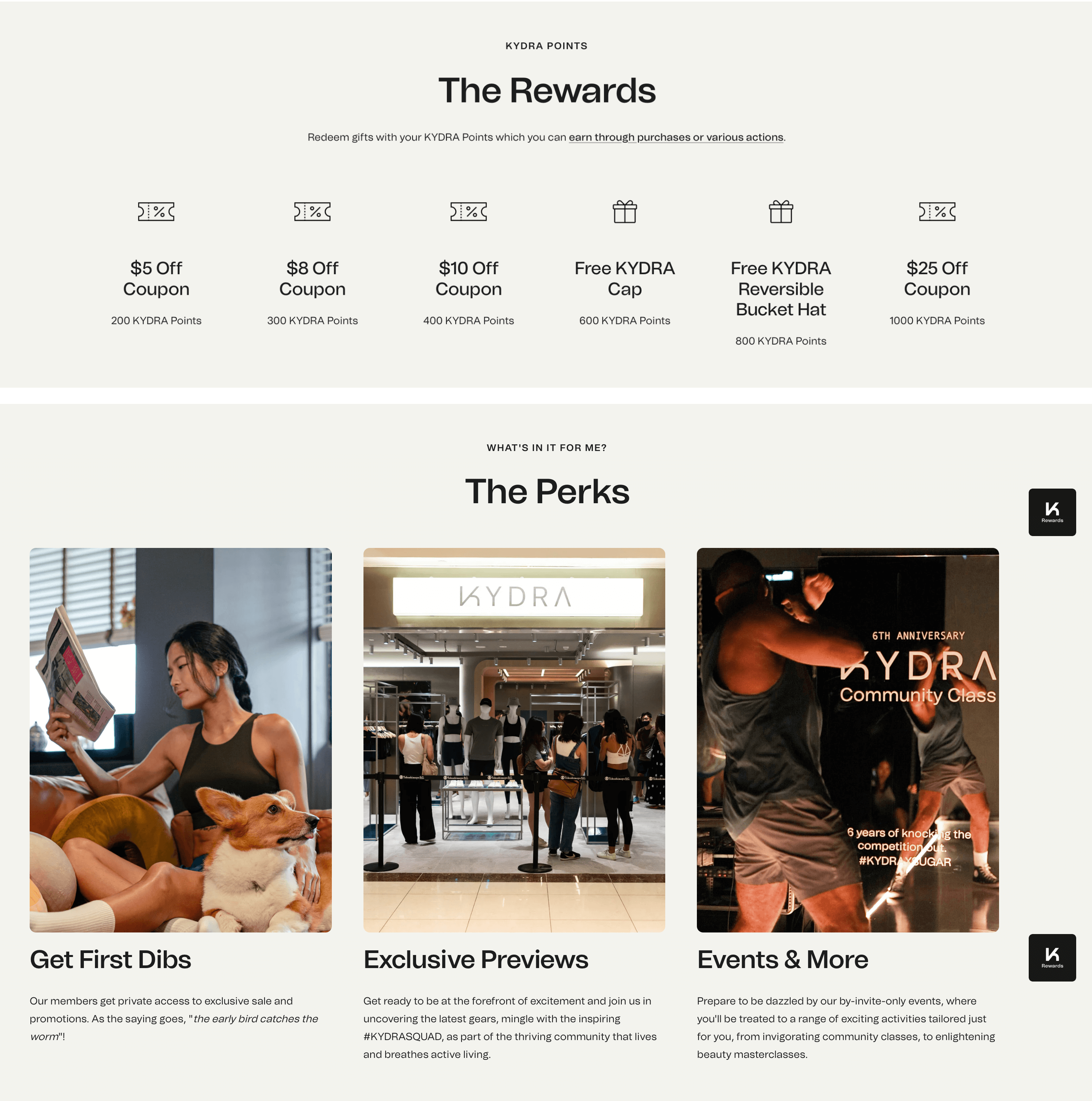
Program highlight: diversified rewards
The key to any great customer rewards program is unsurprisingly great rewards. While you can assume that all of your customers share some similarities, they are all still motivated in different ways. This is why having a wide range of reward types is beneficial, like athletic brand KYDRA. KYDRA Rewards offers a range of transactional and experiential rewards, including financial incentives like amount-based discounts as well as more exclusive benefits like free products, early access to sales, previews of new products, and invites to tailored events like workout classes.
Best loyalty programs in the Toys & Games industry
Mastermind Toys’ Perks Program

Program highlight: best birthday rewards
Any smart toy brand knows that the way into their customers’ hearts is through the smiles on their children’s faces. This is why Mastermind Toys’ Perks program is one of the best customer loyalty programs we’ve seen in the toy industry. After all, is there any day more special to a parent than their kid’s birthday? The brand offers free birthday gifts for their members’ kids, as well as a personalized Birthday Perk and gift guide delivered to their inbox. They also offer free loot bag assembly and expert support to help ensure every birthday is absolutely perfect! This is a prime example of designing your loyalty program with your customers’ values in mind.
Cherry Rewards
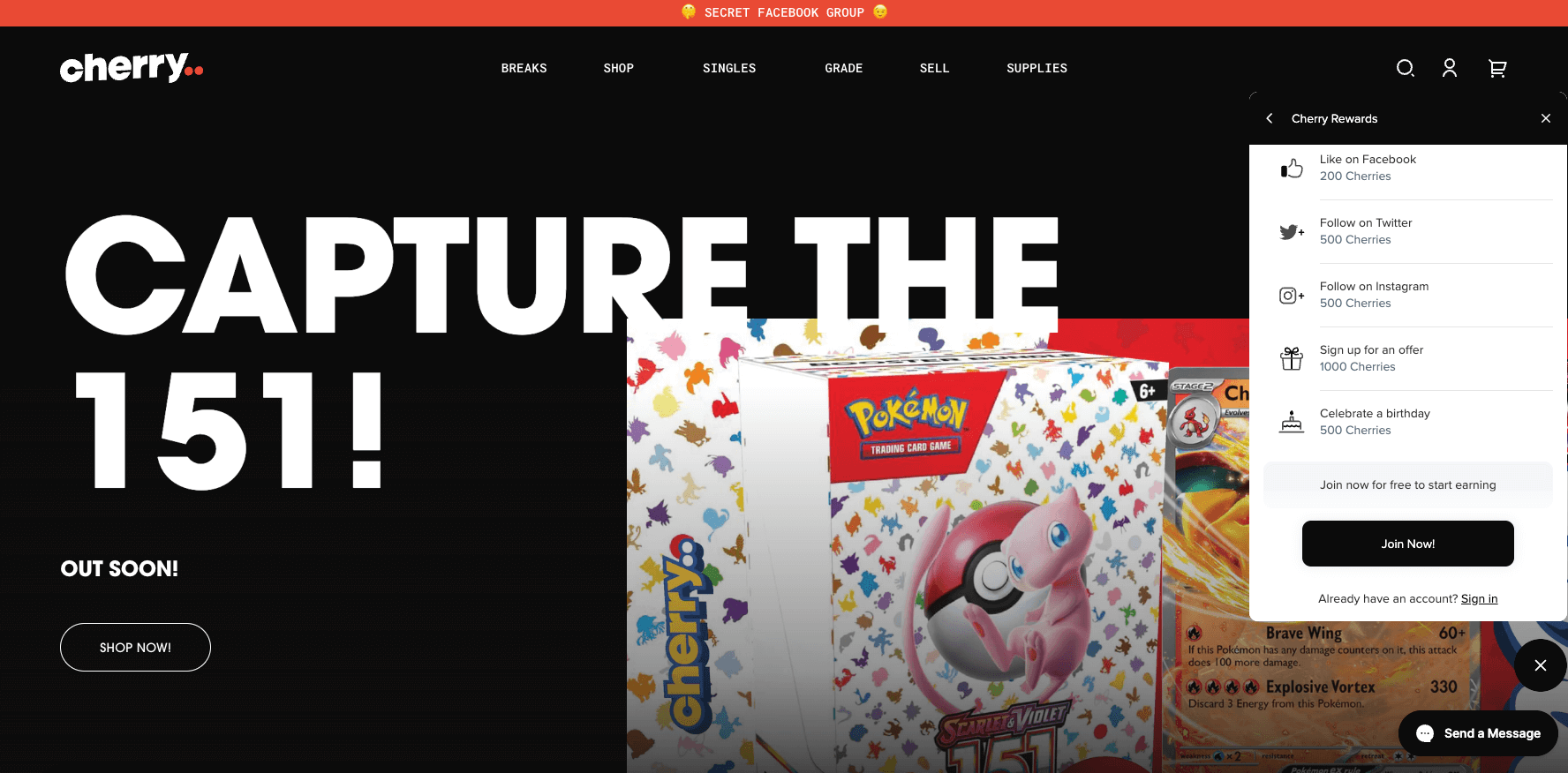
Program highlight: generous points offered for customer data
Toys aren’t just for children. There is a large group of avid toy and playing card collectors who search high and low for the missing pieces they need to complete their collections. Cherry is an Australian toy brand that was started by 2 of these collectors. Cherry uses its loyalty program to collect customer data to deliver personalized communications. They offer a generous 1000 cherries for simply signing up for the program and another 1000 cherries for signing up for an offer. That may seem very high when you consider 1000 cherries equals $10 off, but having information like a customer’s email address and product preferences allows the brand to send custom communications to its customers when a new rare product is available—something that dedicated collectors will appreciate immensely!
Is a rewards program right for you?
Now that you’ve seen some of the best customer loyalty programs around, it’s time to decide if a loyalty program is the missing piece of the puzzle in your customer retention strategy. Review the examples from your industry for inspiration and start configuring a winning customer loyalty program for your ecommerce store today!
Editor’s Note: This post was originally published in December 2014 and was updated for accuracy and comprehensiveness on August 25, 2023.